Blockchain Oracles: How External Data Powers Smart Contracts
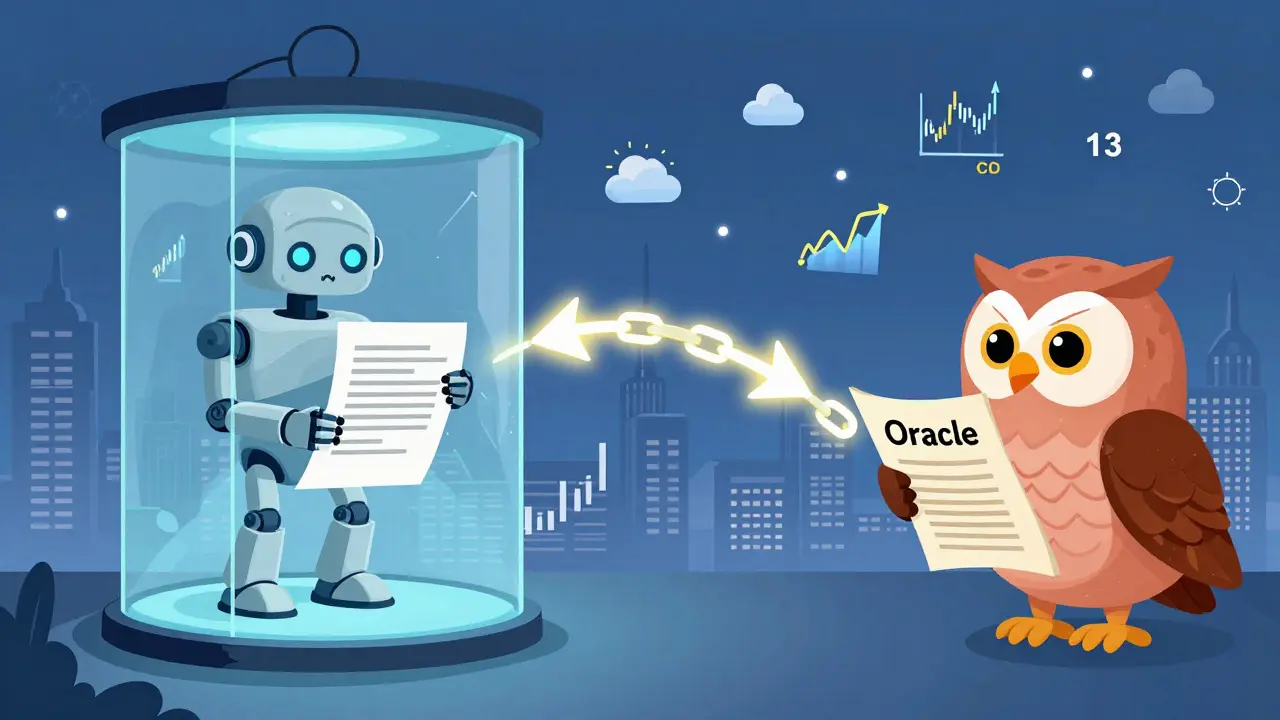
When you hear about blockchain oracles, external data sources that feed real-world information into smart contracts on blockchains. Also known as data oracles, they're the bridge between what happens on-chain and what’s happening in the real world—like the price of Bitcoin, the outcome of a soccer match, or the temperature in a warehouse. Without them, smart contracts would be stuck in a vacuum, unable to react to anything outside their own network. Think of them like a delivery person who brings news to a locked room. The room can’t see outside, but it can act on what’s delivered.
Most DeFi apps rely on oracles to function. When you lend ETH on a platform and earn interest based on the price of ETH, that price doesn’t magically appear on the blockchain. It comes from an oracle. Same with insurance payouts triggered by flight delays, or prediction markets that pay out after an election. Oracles make these automated decisions possible. But they’re also a major weak point. If the data feed is wrong, hacked, or delayed, the whole contract can fail—sometimes with millions at stake. That’s why the best projects use multiple oracles, cross-check data from different sources, and avoid relying on a single provider.
Oracles aren’t just tools—they’re a trade-off. You get automation and trustlessness, but you also inherit the risks of the outside world. Some oracles pull data from centralized APIs like CoinGecko or Yahoo Finance. Others use decentralized networks of independent nodes, like Chainlink, where participants are financially incentivized to report truthfully. The more nodes involved, and the more diverse their data sources, the more reliable the feed. But even the best systems can be fooled by bad data or coordinated attacks. That’s why you’ll see posts here about tokens like DUSD and sUSD—both depend on oracles to maintain their pegs. If the oracle says ETH is worth $1,200 when it’s really $1,800, the stablecoin could collapse.
You’ll also find posts about scams and risky tokens that pretend to use advanced tech like AI or cross-chain oracles—but don’t. Many of these projects are just hype wrapped in jargon. Real oracles are quiet, technical, and critical. They don’t make headlines. They just make sure your smart contract doesn’t pay out $10 million when it should’ve paid $10.
Below, you’ll find real-world examples of how oracles enable—or break—crypto projects. Some are about stablecoins that need constant price updates. Others are about memecoins that claim to use oracles for random outcomes but don’t. You’ll learn which ones actually work, which ones are risky, and how to spot the difference before you invest.
What Are Blockchain Oracles? The Essential Guide to External Data for Smart Contracts
Blockchain oracles connect smart contracts to real-world data like prices, weather, and flight status. Without them, blockchains can't interact with outside systems. Learn how they work, why they matter, and what risks they carry.